Kaizen is a Japanese term that means “continuous improvement” and is often associated with business practices and management philosophies. It indicates everybody’s involvement in the organization to generate value for customers. The concept of Kaizen involves making small, incremental changes regularly to improve processes, products, and overall organizational performance. It is based on the idea that continuous, incremental improvements can lead to significant gains over time.
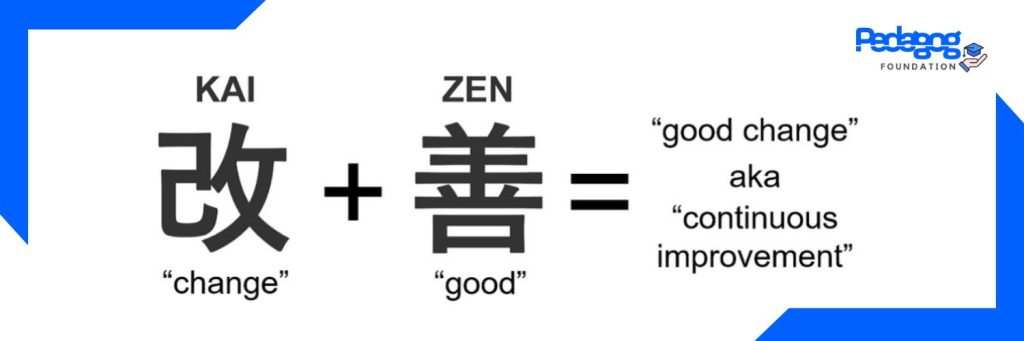
Image credit: https://images.app.goo.gl/wA9NvdueHudZdK9C8
A Kaizen program can be divided into three segments:
- Management-oriented Kaizen: This concentrates on the most strategic and logistic issues and provides the momentum to keep up progress and morale.
- Group-oriented Kaizen: The group-oriented kaizen is a permanent approach and is represented by quality circles and other small group activities.
- Individual-oriented Kaizen: It is manifested in the form of suggestion. It is a kind of morale booster.
The five steps in the Kaizen program are as follows:
a) SEIRI: Straighten up
b) SEITON: Put things in order
c) SEISO: Clean up
d) SEIKETSU: Personal cleanliness
e) SHITSUKE: Discipline
Here are some key aspects of Kaizen theory: It talks about the following
- Continuous Improvement: Kaizen focuses on making gradual improvements rather than aiming for big, sudden changes. The idea is that when made consistently, small changes can lead to substantial improvements over time.
- Employee Involvement: Kaizen encourages the involvement of all employees in the improvement process. Everyone, from top management to front-line workers, is encouraged to contribute ideas for improvement. This inclusive approach helps in identifying inefficiencies and finding solutions. It also helps to enhance the idea of collaboration and group dynamics.
- Elimination of Waste: Kaizen aims to eliminate waste (in terms of time, materials, and effort) and improve efficiency. This includes identifying and addressing any non-value-adding activities in a process.
- Standardization: Once a process improvement is identified and tested, it is standardized and documented so that the new, better way of doing things becomes the new norm. This helps in ensuring consistency and sustained improvement.
- Quality Control: Kaizen often involves close attention to quality control. By continuously monitoring and improving processes, the overall quality of products and services can be enhanced.
- Problem Solving: Kaizen encourages proactive problem-solving. By addressing issues as they arise and implementing solutions, organizations can avoid recurring problems and enhance their processes.
- Feedback and Reflection: Regular feedback and reflection are integral to the Kaizen approach. Organizations continually assess the effectiveness of improvements and adjust as needed.
- Cultural Aspect: Kaizen is not just a set of tools or techniques; it is also a cultural approach. It requires a mindset that values ongoing improvement and encourages a culture of learning and development.
The Kaizen process cycle is frequently referred to as PDCA (Plan, Do, Check, and Act). PDCA brings a scientific approach to making improvements:
Plan: develop a hypothesis
Do: run experiment
Check: evaluate results
Act: refine your experiment; then start a new cycle
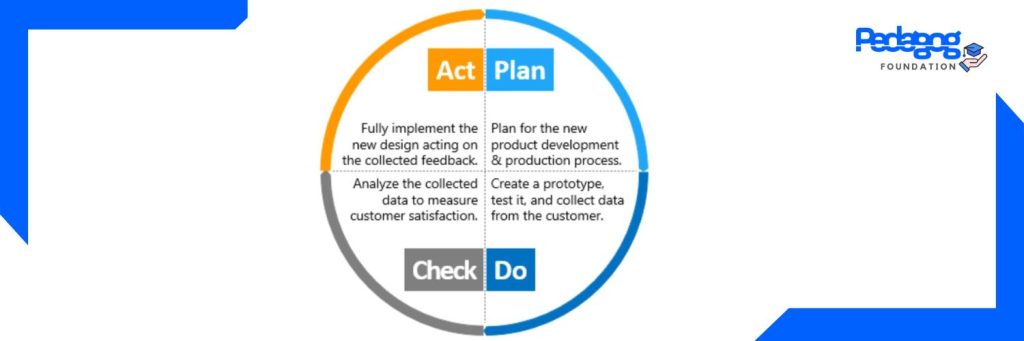
Image credit: https://images.app.goo.gl/vMaN7vUTgJ79Qqbc8
Why Kaizen is crucial in business?
Kaizen is crucial in business for several reasons, primarily because it fosters a culture of continuous improvement and efficiency.
- Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity: By focusing on incremental improvements, Kaizen helps businesses streamline processes, eliminate waste, and optimize resource use. This leads to increased efficiency and productivity, allowing companies to do more with less.
- Improved Quality: Continuous improvement efforts under Kaizen help in identifying and addressing quality issues systematically. This leads to better products and services, meeting or exceeding customer expectations and enhancing the overall quality.
- Cost Reduction: Kaizen’s emphasis on eliminating waste and improving processes often results in cost savings. By reducing inefficiencies and optimizing operations, businesses can lower production costs and improve profitability.
- Employee Engagement and Morale: Involving employees in the improvement process boosts their engagement and morale. When employees see that their ideas are valued and contribute to positive changes, they are more motivated and committed to their work.
- Customer Satisfaction: By continually improving products and services, businesses can better meet customer needs and expectations. This leads to higher customer satisfaction, which can translate into increased customer loyalty and repeat business.
- Competitive Advantage: Businesses that embrace Kaizen can adapt more quickly to changes in the market, innovate continuously, and stay ahead of competitors. This adaptability and ongoing improvement can provide a significant competitive edge.
- Problem Solving and Innovation: Kaizen encourages a proactive approach to problem-solving and innovation. By regularly evaluating processes and seeking improvements, businesses can address issues before they become major problems and foster a culture of innovation.
- Consistency and Standardization: Implementing Kaizen leads to standardized processes that ensure consistency in quality and performance. This standardization helps in maintaining high standards and streamlining operations.
- Long-Term Success: Continuous improvement through Kaizen helps build a foundation for long-term success. It creates a dynamic environment where businesses are always evolving and adapting, which is essential for sustained growth and resilience.
- Cultural Transformation: Kaizen promotes a culture of learning, collaboration, and responsibility. It shifts the focus from merely reacting to problems to proactively seeking improvements, creating a positive organizational culture.
In conclusion, I must add that the practice of Kaizen theory helps to analyze the SWOT of a business. SWOT is a very common abbreviation for operation managers. It indicates Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats to any organization. By practicing Kaizen, businesses can grow healthily.
Submitted by: Dr. Rohit Kumar Pal
Senior Academician
Pedagog

